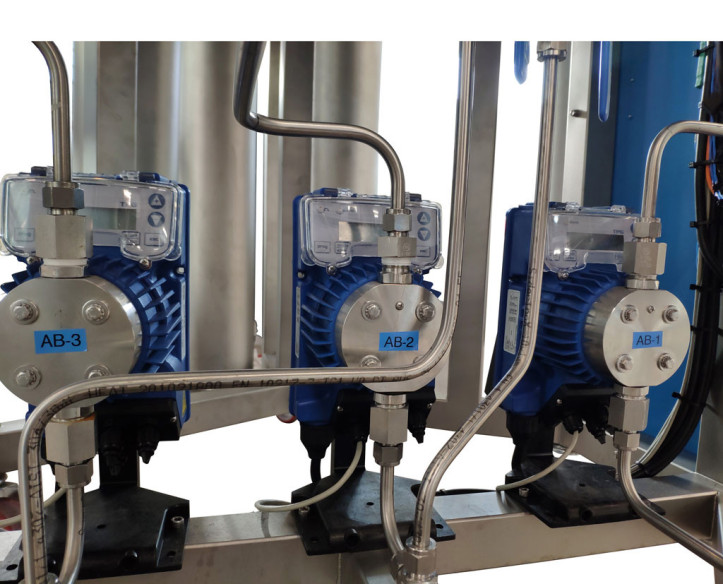
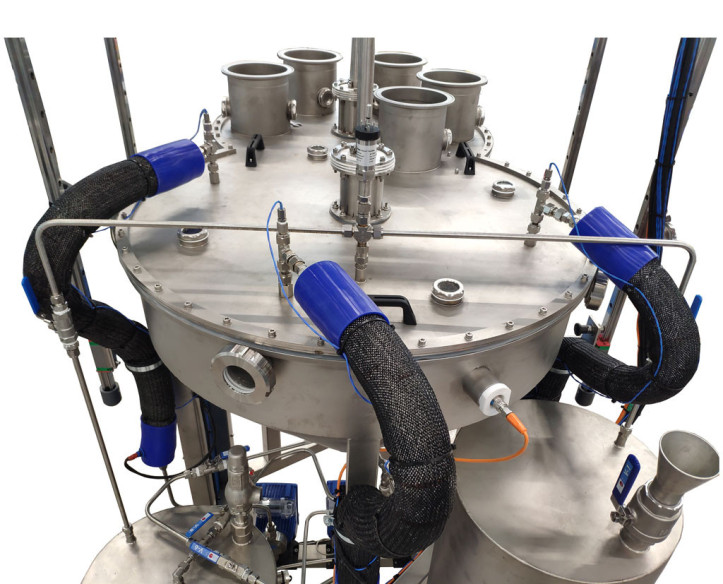
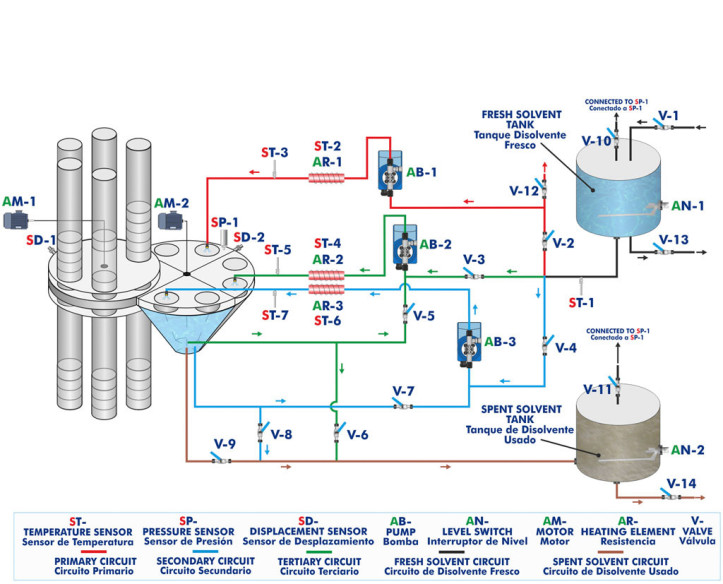
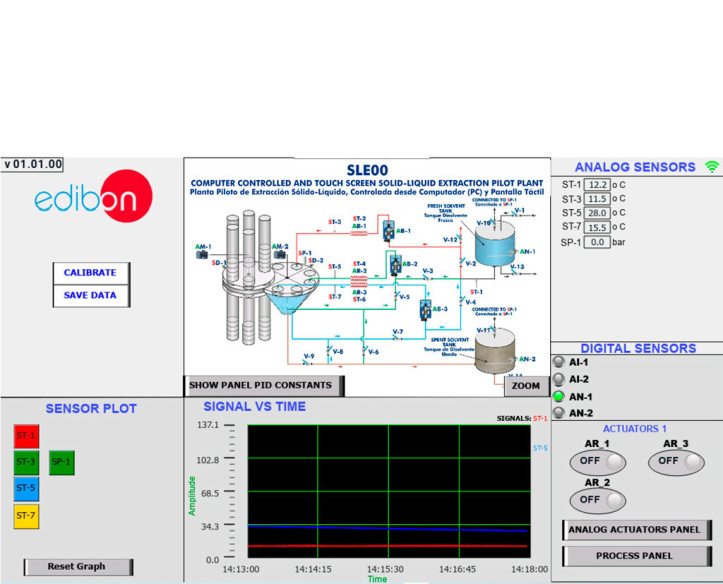
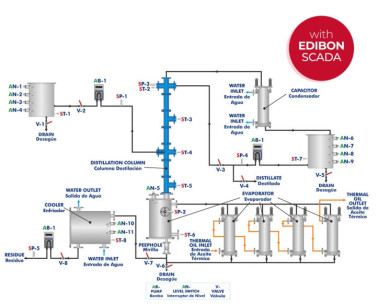
Pilot plants are small-scale processing plants designed to simulate industrial or research processes before large-scale implementation. They are essential for testing technologies, optimizing processes, and validating models before investing in mass production. These plants allow researchers and...
In a world where energy demand continues to rise and non-renewable resources are rapidly depleting, the need for sustainable, environmentally friendly solutions has never been more urgent. The circular economy and the use of organic biomass to produce biofuels are emerging as key answers to...
Direct Air Capture (DAC) is an innovative technology that removes CO₂ directly from the air using chemical reactions with liquid solvents or solid absorbents. Despite challenges such as high costs and energy consumption, DAC offers a potential solution to reduce atmospheric CO₂ concentrations and...
We want to present you the new pilot plant that we have developed adapting to the needs of the department of Chemical Engineering at the Technical University of Denmark (DTU)
 Cookie preferences
Cookie preferences