- Beranda
- Produk
- 1.- FISIKA
- PROGRAM AKADEMIK
- PENDIDIKAN TEKNIS TINGGI
- TEKNIK MAKANAN
- TEKNIK TOPOGRAFI
- GEOLOGI
- TEKNIK HUTAN
- TEKNIK LINGKUNGAN
- TEKNIK EKOLOGI
- TEKNIK TEKSTIL
- TEKNIK UNTUK INDUSTRI PERTANIAN
- TEKNIK MESIN
- KIMIA
- TEKNIK KIMIA
- TEKNIK PROSES
- TEKNIK GEOLOGI, PERTAMBANGAN DAN MINYAK
- PUSAT PELATIHAN PETROLEUM
- TEKNIK NAVAL
- TEKNIK PERTANIAN
- TEKNIK ELEKTRONIK
- ARSITEKTUR
- ILMU KOMPUTER DAN TEKNIK
- TEKNIK NUKLIR
- TEKNIK OTOMATIS
- TEKNIK ENERGETIK
- PUSAT PELATIHAN ENERGI
- TEKNIK LISTRIK
- TEKNIK SISTEM
- TEKNIK PENERBANGAN
- TEKNIK LAUT DAN ILMU LAUT
- FISIKA
- TEKNIK INDUSTRI
- PUSAT INTERNASIONAL UNTUK PELATIHAN TEKNIS, PENGEMBANGAN DAN PENELITIAN
- TEKNIK BAHAN
- TEKNIK LOGAM
- TEKNIK SIPIL
- TEKNIK TELEKOMUNIKASI
- TEKNIK TERMAL
- SEKOLAH TEKNIS
- ELEKTRONIK
- KOMUNIKASI
- LISTRIK
- ILMU KOMPUTER DAN TEKNIK
- TEKNOLOGI OTOMOTIF
- TEKNIK SIPIL
- MEKANIK DAN INDUSTRI
- MEKANIK DAN LOGAM
- MEKANIKA CAIRAN
- REFRIGERASI DAN AC
- KIMIA INDUSTRI
- KIMIA
- TEKNOLOGI MAKANAN
- PERTANIAN
- AGROINDUSTRI
- PEMELIHARAAN
- MARITIM DAN PERIKANAN
- PERAWATAN PENERBANGAN
- INSTRUMENTASI DAN KONTROL
- LINGKUNGAN
- TEKNOLOGI
- TEKNOLOGI KONSTRUKSI
- TEKNOLOGI ELEKTROMEKANIK
- TEKNOLOGI DESAIN STRUKTURAL
- TEKNOLOGI PRODUKSI INDUSTRI
- TEKNOLOGI INFORMASI
- PENGENDALIAN KUALITAS
- TEKNOLOGI SISTEM ENERGI
- TEKNOLOGI PERTAMBANGAN DAN MINYAK BUMI
- TEKNOLOGI GAS ALAM
- ENERGI TERBARUKAN
- TEKNOLOGI TELEKOMUNIKASI
- TEKNOLOGI MEKANIK
- TEKNOLOGI ANGIN
- TEKNOLOGI NUKLIR
- TEKNOLOGI KONTROL PROSES
- TEKNOLOGI LAYANAN UMUM
- TEKNOLOGI LABORATORIUM
- OTOMATISASI DAN MEKATRONIKA
- TRANSPORTASI DAN LOGISTIK
- PENDIDIKAN TEKNIS TINGGI
- 2.- ELEKTRONIKA
- 3.- KOMUNIKASI
- 4.- LISTRIK
- 5.- ENERGI
- 5.1.- GRID CERDAS DAN SISTEM DAYA
- 5.2.- MIKROGRID
- 5.3.- ENERGI TERBARUKAN
- 5.3.1.- ENERGI SURYA FOTOVOLTAIK
- 5.3.2.- ENERGI TERMAL SURYA
- 5.3.3.- ENERGI ANGIN
- 5.3.4.- ENERGI LAUT
- 5.3.5.- ENERGI GEOTHERMAL
- 5.3.6.- ENERGI HIDROLIK
- 5.3.7.- BIOFUEL
- 5.3.8.- SISTEM AKUMULASI ENERGI
- 5.3.9.- SEL BAHAN BAKAR HYDROGEN
- 5.3.10.- TURBIN STEAM DAN SIKLUS RANKINE ORGANIK
- 5.3.11.- SISTEM NON-KONVENSIONAL LAINNYA
- 5.4.- ENERGI KONVENSIONAL
- 5.5.- PENYIMPANAN ENERGI
- 5.6.- TEGANGAN TINGGI DAN SISTEM PERLINDUNGAN LISTRIK
- 5.7.- PEMASANGAN DAN PEMELIHARAAN
- 6.- MEKATRONIK & OTOMASI
- 7.- MEKANIKA
- 8.- MEKANIKA FLUIDA
- 9.- TERMODINAMIK DAN TERMOTEKNIK
- 10.- PENGENDALIAN PROSES
- 11.- TEKNIK KIMIA
- 11.1.- OPERASI UNIT
- 11.1.1.- FLUIDIZATION
- 11.1.2.- PENGUAPAN
- 11.1.3.- MENDIDIH
- 11.1.4.- DISTILASI DAN RETAK
- 11.1.5.- EKSTRAKSI
- 11.1.6.- DIFUSI
- 11.1.7.- PENGERINGAN DAN PENDINGINAN
- 11.1.8.- PENYERAPAN DAN ADSORPSI
- 11.1.9.- PERTUKARAN ION DAN KOROSI
- 11.1.10.- KRISTALISASI DAN PIROLISIS
- 11.1.11.- FILTRASI, SEDIMENTASI, DAN PENCAMPURAN
- 11.1.12.- PENGOBATAN SOLIDS
- 11.2.- REAKTOR KIMIA
- 11.1.- OPERASI UNIT
- 12.- TEKNOLOGI PANGAN & AIR
- 13.- LINGKUNGAN HIDUP
- 14.- TEKNIK BIOMEDIS
- AKSESORIS LABORATORIUM
- PABRIK PILOT SESUAI PESANAN
- MODUL
- EKSPANSI
- LABORATORIUM
- Garis Bisnis
- Teknologi
- Unduh
- Tentang kami
- Berita
- KONTAK
Biomedical engineering and its importance for the medical sector.
What is biomedical engineering?
When did biomedical engineering begin?
Formal biomedical engineering as a field began to take shape in the 1950s and 1960s. As medical technology and healthcare advanced, there emerged a need to apply engineering principles to medicine, aiming to enhance patient diagnosis, treatment, and care. While the concepts and collaboration between engineers and medical professionals had existed before, it was during this period that specific academic programs in biomedical engineering began to be established.
Since then, biomedical engineering has significantly expanded, encompassing a wide range of application areas including medical instrumentation, medical imaging, biomechanics, bioinformatics, medical devices, nanotechnology in medicine, and more. As technology continues to progress and medical needs evolve, biomedical engineering continues to grow and play an essential role in developing innovative solutions for the healthcare field.
What is the main goal of biomedical engineering?
The primary objective of biomedical engineering is to enhance the quality of healthcare, streamline disease diagnosis and treatment, and develop medical devices and systems that contribute to enhancing the health and well-being of individuals.
What does a biomedical engineer do?
Biomedical engineers operate across a broad spectrum of domains, such as designing cutting-edge medical equipment, advancing medical imaging technologies like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans, crafting prosthetics and assistive devices for individuals with disabilities, researching diagnostic systems, managing health data, and implementing medical technologies within clinical settings.
As such, a strong understanding of both engineering principles and biology and medicine is requisite. Professionals in this field collaborate closely with physicians, scientists, and other healthcare experts to devise innovative solutions that benefit both patients and medical professionals.


What do we do at EDIBON to contribute to the learning and research of biomedical engineers?
After many years of research and collaboration with professors and researchers, at EDIBON, we have developed educational and research equipment to assist in the learning process during the formative stage and to aid research in this rapidly growing and evolving field.
For this reason, we offer training equipment that can be installed in laboratories, complementing theoretical studies from the beginning with biomechanics (studying the mechanics of movement and understanding the movement of living organisms, including human body movement). This is followed by electronics applied to biomedical engineering, enabling sufficient knowledge for the subsequent development of biomedical instrumentation. The process culminates with biomedical equipment to comprehend the functioning of materials used in places such as hospitals and healthcare centers.
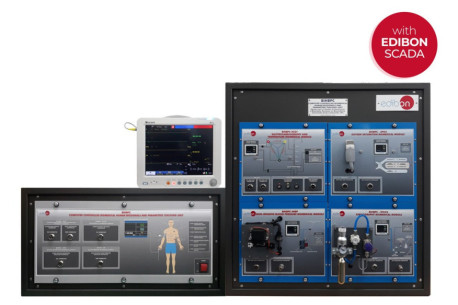
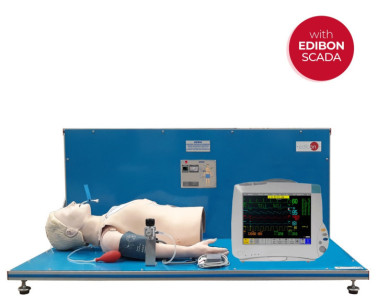
Equipment like our Computer Controlled Human Biosignals and Parameters Teaching Unit (BIHBPC), Computer Controlled Biomedical Patient Biosignals Simulator (BIPBSC), Computer Controlled Spirometry Teaching Unit (BISBC), Computer Controlled Biomedical Circulatory System Teaching Unit (BICSC) and Unit for Study of Electrosurgery in Biomedicine (BICIR), assist students, professors, and researchers in advancing this remarkable discipline.
 Preferensi cookie
Preferensi cookie