At EDIBON, we are committed to strengthening skills as a strategic pillar for the competitiveness and social well-being of the European Union. Proper training not only boosts the economy but also enables individuals to fully participate in society and democracy.
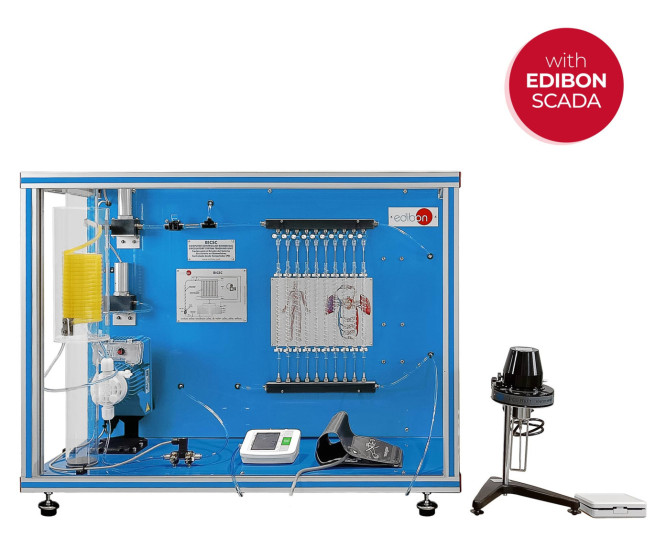
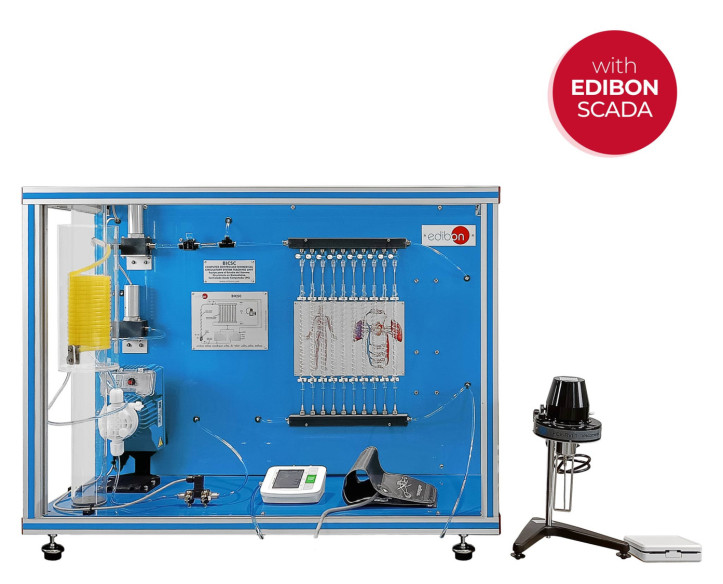
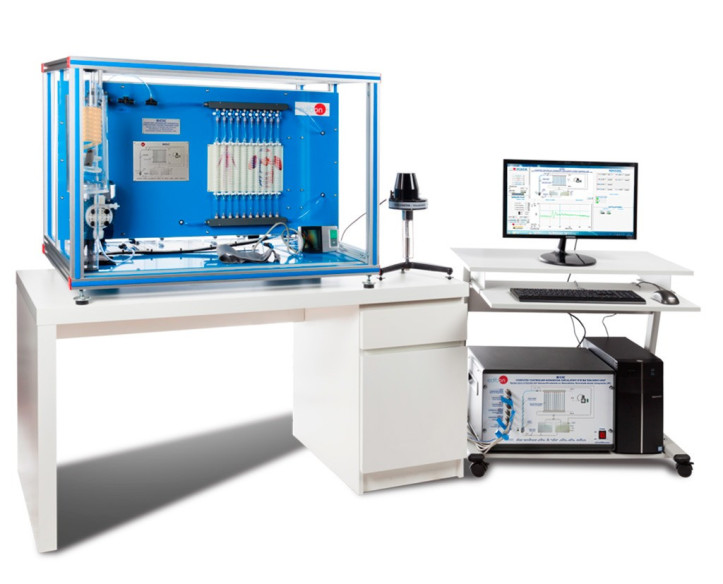
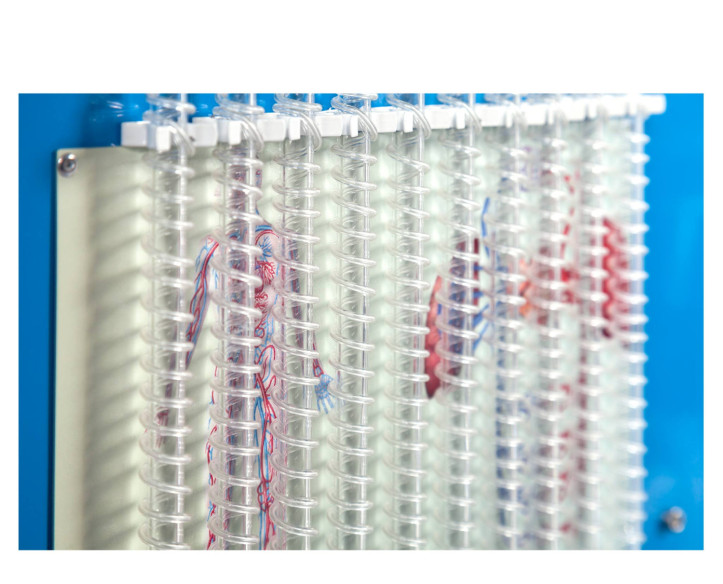
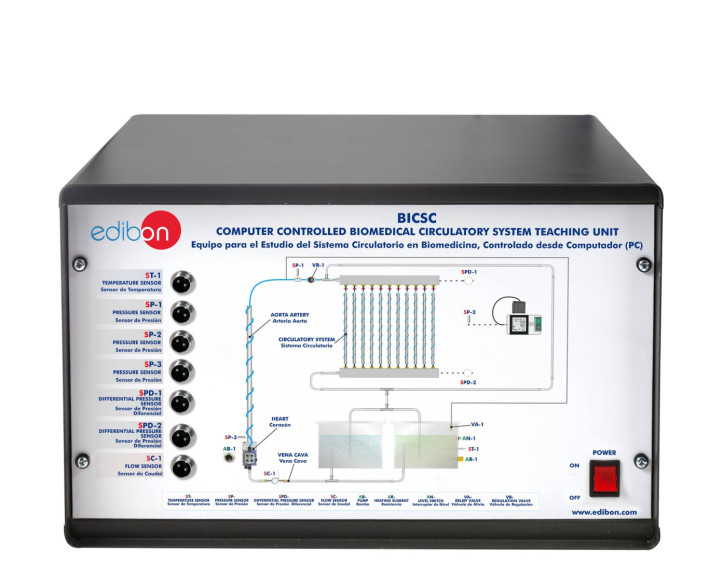
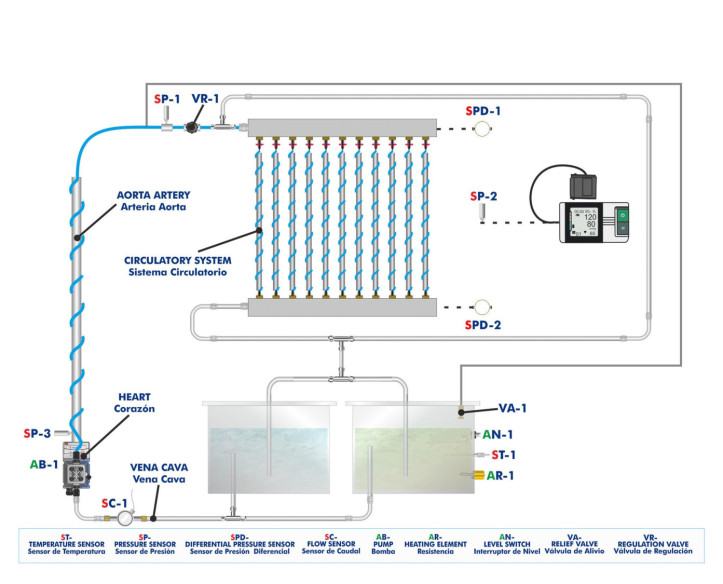
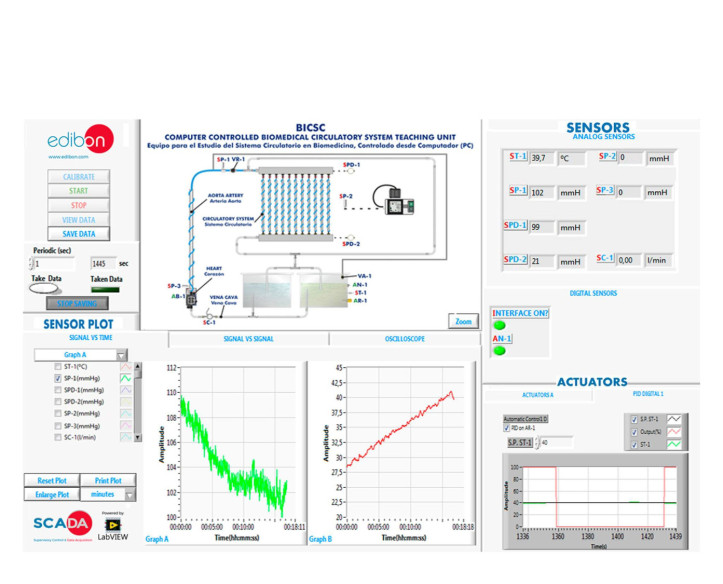
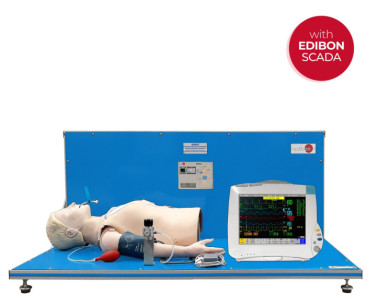
Biomedical engineering is an interdisciplinary field that synergizes principles from both engineering and biology to design, develop, and sustain technological solutions tailored for medical and healthcare applications.
A few days ago we carried out our last installation at Universidade de Vigo. It was a pleasure to share time with the electronic engineering department, who will now be able to enjoy the benefits of studying and researching with the new equipment installed: the Computer Controlled Biomedical...
 Preferensi cookie
Preferensi cookie