At EDIBON, we are committed to strengthening skills as a strategic pillar for the competitiveness and social well-being of the European Union. Proper training not only boosts the economy but also enables individuals to fully participate in society and democracy.
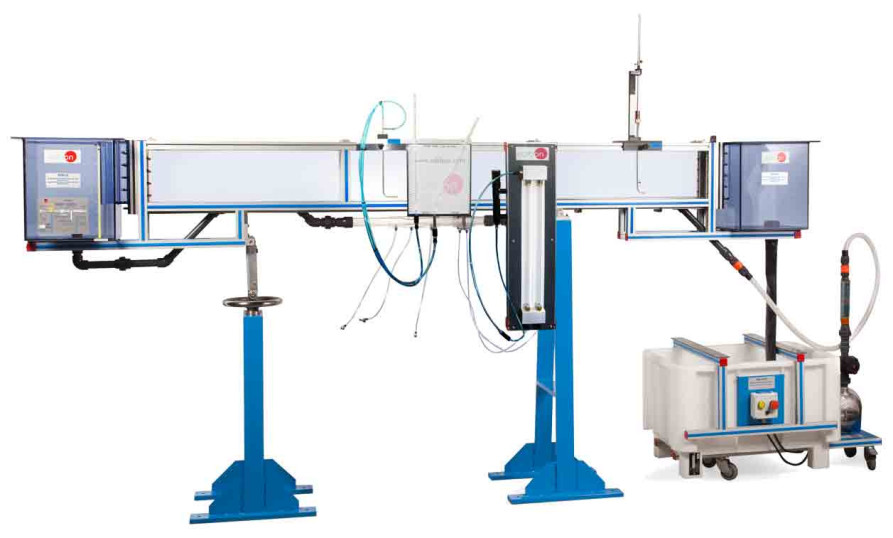
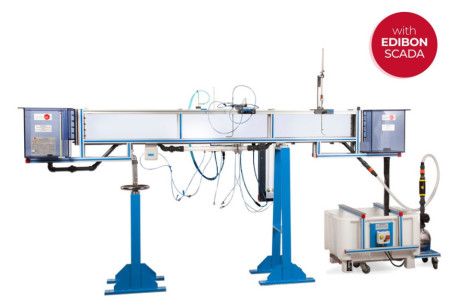
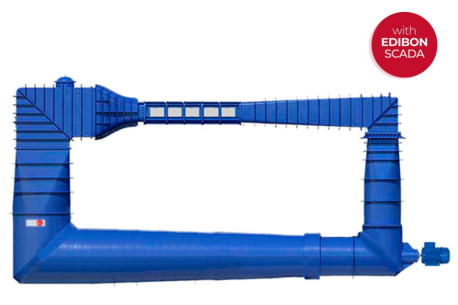
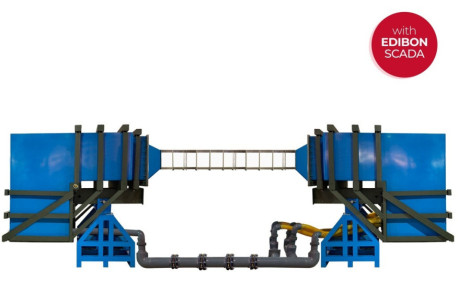
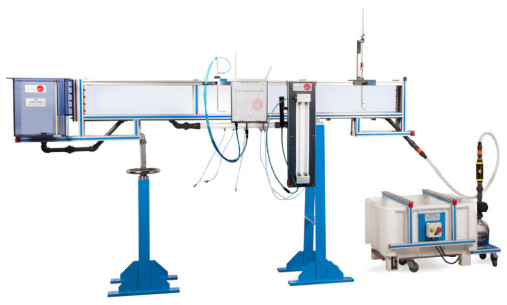
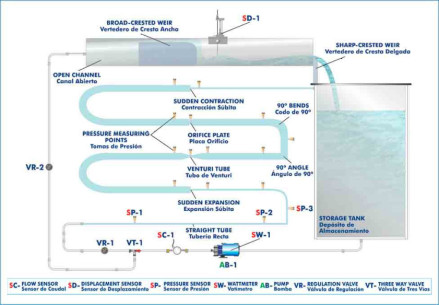
We want to present our new installation in the Faculté des Sciences at the Université d’Etat d’Haiti, specifically in the Fluid Mechanics Department. There, we have installed many of our equipment, among which are: AFT, CF80/5 (with CFAS, CFFS, CFPLR, CFPR, CFRM, CFSDL, CFTP, CFTS, CFVD, CFVEN,...
Are you a teacher or do you work as an engineering researcher? EDIBON offers courses for teachers and #research staff. Take a look at the course of Fluid Mechanics and learn about #fluids properties. #DiscoverEdibon #Engineering.
 Preferências de cookies
Preferências de cookies