An electronic filter is an element that allows electrical signals to pass through it, at a specific frequency or frequency ranges while preventing the passage of others, being able to modify both, their amplitude and phase. It is a device that separates, passes or suppresses a group of signals from a mixture of signals.
Filters are two-port systems, one input and one output, operating in the frequency domain. Their operation is based on blocking signals in terms of their spectral content, letting through signals whose frequency is within a certain range known as the pass band and rejecting those signals outside this range, known as the rejection band. A filter works on input signals to produce an output signal whose spectral content depends on the type of filter.
A frequency filter is a circuit that uses electrical and/or electronic components to attenuate, correct or reject a range of frequencies within any type of signal. This range can be different from time to time as filters are very flexible and different types exist.
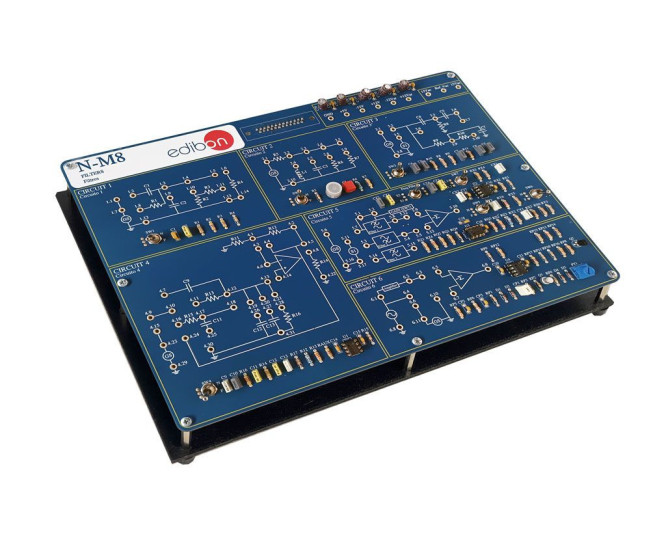
With Filters Module, "N-M8", designed by EDIBON, the different types of filters can be studied: RC and LC, in "T" type configuration, active filters and also study associations of one and others in order to be able to practice with more complex filters, to obtain other filters with certain desired characteristics (low-pass filter, high-pass, band-pass and eliminated band).
In addition, faults can be simulated in most of the circuits under study. The student must investigate what is happening in the circuit and why it is not working properly. These faults simulations can be of several types from damage components to a hypothetical incorrect circuit assembly.
 Preferências de cookies
Preferências de cookies