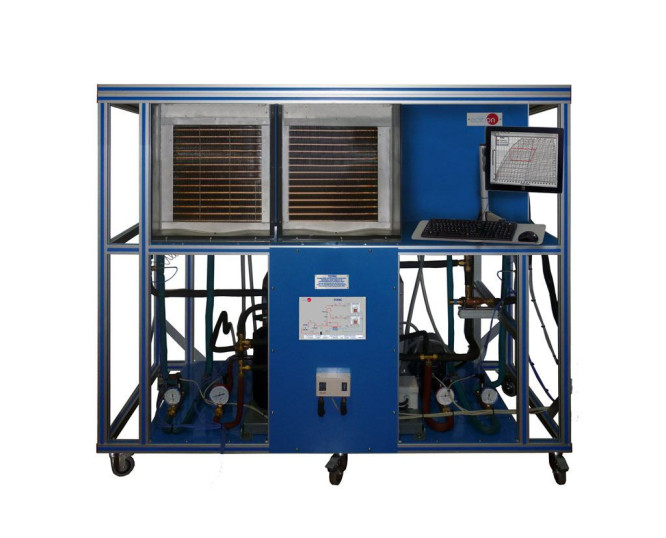
The Computer Controlled Capacity Control and Faults in Refrigeration Systems, "TCFRC", has been designed by EDIBON to explore various power regulation techniques and simulate typical failures in refrigeration systems.
Power regulation is crucial for optimizing energy efficiency, adjusting cooling capacity to actual demand, and improving process efficiency by ensuring that components like compressors and evaporators operate within their optimal ranges. The Computer Controlled Capacity Control and Faults in Refrigeration Systems, "TCFRC", allows for the investigation of these control methods and the analysis of system behavior under both normal conditions and up to 18 fault scenarios, such as defective valves or blocked pipes.
In this unit, the components of a refrigeration circuit are clearly laid out, including refrigeration and freezing chambers. In these circuits, both temperature and humidity can be measured for improved system control.
To facilitate understanding, the pipes are color-coded in red and blue to indicate hot and cold water circuits, and they are insulated to ensure an efficient process. Additionally, the equipment incorporates a diagram on the front panel for clearer and more precise process monitoring.
The "TCFRC" includes solenoid valves that allow for separate or parallel operation of the evaporators in both chambers. Furthermore, the circuit is equipped with a compressor, a condenser, a power controller that adjusts the system's power supply, a start-up controller, and a combined pressure switch for the compressor’s pressure, suction, and discharge sides.
Each chamber has an evaporator, solenoid valve, temperature control thermostats, a thermostatic expansion valve that regulates the refrigerant flow to the evaporator by adjusting the amount of refrigerant based on temperature, thus ensuring an efficient and controlled refrigeration process, a fan, heater, heat exchanger for subcooling the refrigerant used, and evaporation pressure control. A heat exchanger at the inlet of both evaporators allows for the investigation of refrigerant subcooling in relation to process efficiency. The cooling power of the two chambers, separately, is controlled by a thermostat. Additionally, the refrigeration chamber includes an evaporation pressure regulator.
The freezing chamber has two defrosting methods: an electric system and a hot gas system, with the latter using hot refrigerant from the compressor.
Failures are activated on a touch screen connected to the computer (PC), which allows:
- Direct transmission from the computer to the touch screen for fault activation and data acquisition.
- Representation of the thermodynamic cycle in the log p-h diagram.
- Recording of test measurements over time and generation of a file compatible with spreadsheet applications.
The most important objectives of this equipment are:
- Familiarization with key devices for varying cooling power:
- Thermostat.
- Power controller.
- Start-up controller.
- Combined pressure switch for the compressor’s pressure, suction, and discharge sides.
- Fault localization in refrigeration system components.
- Effect of refrigerant subcooling.
- Familiarization with defrosting methods:
- Defrosting using an electric heater.
- Defrosting using hot gas.
- Representation of the thermodynamic cycle in the log p-h diagram.
This Computer Controlled Unit is supplied with the EDIBON Computer Control System (SCADA), and includes: The unit itself + Touch Screen + Computer Control, Data Acquisition and Data Management Software Packages, for controlling the process and all parameters involved in the process.
 Настройки cookie
Настройки cookie