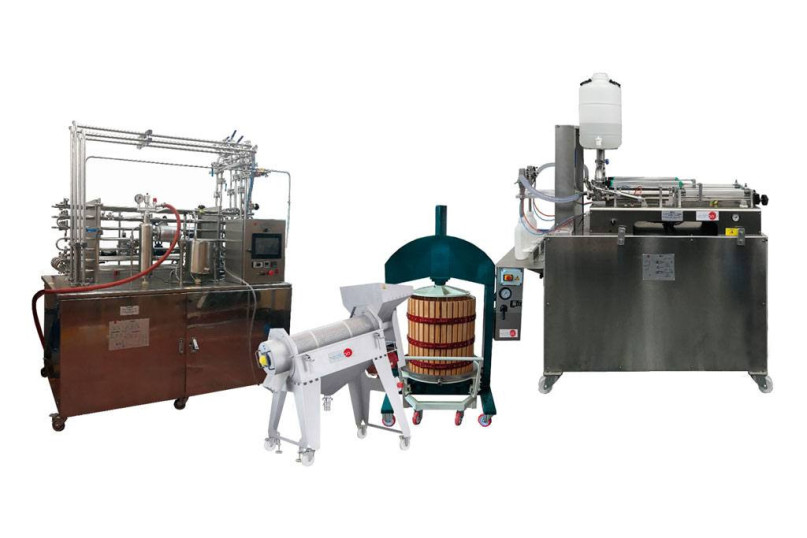
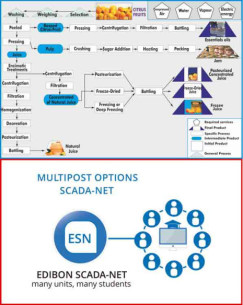
The Pilot Plant for Concentrated Juice Production, "FR00/JC", is a scale size pilot-plant equipped to carry out all industrial stages of concentrated juice production.
In the production plant of concentrate juices, the process begins with the reception of fresh fruit, where a meticulous process of selection, washing, and preparation of the fruit is carried out. To carry out these stages in the pilot plant, the following unit is included:
- WMFV. Washing Machine for Fruit and Vegetables. Fruit washing is essential to ensure hygiene and food safety. Its function is to remove any dirt, residue, or surface contaminants from the fresh fruit, ensuring that it is clean and ready for processing. In addition, during this process, pieces of fruit that do not meet the quality standards for consumption are discarded. Once the selection is complete, the fruit is peeled if necessary, preparing it for the next step: juice extraction.
- FPCR. Fruit Pitting and Crushing Unit. The process of preparing the fruit involves pitting and crushing the fruit to break the cells and release the juice to obtain the juice efficiently, which represents a key role in the fruit preparation stage. It crushes the fruit and, if necessary, removes the pits, which facilitates juice extraction and ensures greater efficiency in the process.
The next step in juice extraction is the pressing of the crushed fruit, where two alternative units are available: the Sheet Press for Liquid Products Extraction, "SPLE" and the Hydraulic Press for Liquid Product Extraction, "HPLE". In this way, the pilot plant includes one of the two pressing units mentioned above, depending on the type of pressing required.
- SPLE. Sheet Press for Liquid Products Extraction. The manual sheet press is used to separate the juice from the pulp and the solids from the crushed fruit. Its manual operation allows a more precise control of the process and is ideal for smaller production batches.
- HPLE. Hydraulic Press for Liquid Product Extraction. Another form of pressing is the hydraulic press, which is a larger and automated version of the manual press. It provides uniform and controlled pressure on the crushed fruit, which facilitates efficient juice extraction and effective solids separation.
Pressing is a crucial step in separating the juice from the pulp and large fruit solids. The result is a liquid product free of large solid particles, along with the fruit pulp.
The extracted liquid is then undergoes to a separation process, where it is passed through the centrifuge, which plays a crucial role in the juice concentrate production process by facilitating clarification and filtration of the product.
- PJCM. Pulp and Juice Centrifugal Machine for Juices and Agri-food Products. This unit uses centrifugal force to separate the solid and liquid particles present in the juice, allowing the elimination of impurities and obtaining a cleaner, clearer liquid. During this step, the centrifuge helps to remove pulp, seeds, residues, and other unwanted solids from the juice, thus improving its quality and visual appearance. In addition, by reducing the amount of suspended solids, the centrifuge helps to avoid potential sedimentation problems and improve the stability of the final product. This results in a high-quality product.
The liquid obtained is treated in a filter to remove the residual solids contained in the liquid, thus obtaining a clarified liquid.
- SFAF. Sheet Filter for Agri-food Liquid Products. The sheet filter is essential to remove any remaining solid residue from the juice, ensuring that the final product is clear and free of undesirable particles, which improves its appearance and organoleptic quality.
Once the fruit has been pressed and treated, the product is concentrated in an evaporator. The evaporator is key in the concentrated juice production process by allowing the concentration of the liquid through the controlled elimination of water.
- ECAL/CTS. Computer Controlled and Touch Screen Evaporator for Concentrating Agri-food Liquid Products. This unit uses heat to evaporate the water from the juice, which increases the concentration of solids and sugars. This concentration is essential to reduce the volume of the product and improve its nutrient content and flavor. The evaporator offers flexibility by adjusting the concentration according to the requirements of the final product and removes unwanted volatile compounds, improving the flavor and aroma of the juice. It also improves the shelf life of the juice concentrate.
The product obtained is then undergoes to a pasteurization process, where two alternative units are available: the Computer Controlled and Touch Screen UHT Unit, "AUHT/CTS" and the Computer Controlled Teaching Autonomous Pasteurization Unit, "PADC". In this way, the pilot plant includes one pasteurization unit of the two mentioned previously, according to the needs of the process. This step is essential to ensure the proper preservation of the product, extending its shelf life and maintaining its freshness and natural flavor. There are three different processes: VAT or slow pasteurization, High temperature short time pasteurization (HTST) and Ultra-High Temperature pasteurization (UHT).
AUHT/CTS. Computer Controlled and Touch Screen UHT Unit. It is a compact design and easy installation pilot plant that works as independent unit or as part of an integrated process finishing that allows for studying in depth the UHT (at Ultra-High Temperature) pasteurization process of products and the variables of the process.
PADC. Computer Controlled Teaching Autonomous Pasteurization Unit. An alternative to the previous pasteurization unit is the Computer Controlled Teaching Autonomous Pasteurization Unit, "PADC". Allows to study VAT or slow pasteurization and its process variables. The unit receives juice from a refrigeration tank (not included) and this is impelled with a pump (computer controlled). It is heated in the heat exchanger, by counter-current flow, with hot water coming from a circuit formed by a water tank with a heating element (computer controlled), a water pump (computer controlled), a manometer, a security valve, an expansion vessel, a purge valve and a pressure regulator, until reaching the established pasteurization temperature.
Both pasteurizers are used to heat the juice to a temperature sufficient to eliminate harmful bacteria and microorganisms, without compromising the flavor and nutrients of the juice. This process helps to extend the shelf life of the product without significantly altering its properties.
The filtered and treated product is bottled using a bottling and capping machines. The plant has two alternative bottling machines: the Computer Controlled Liquid Packaging Teaching Unit, "EDLC" and the Bottling Machine for Agroalimentary Liquid Products, "BMAF". Therefore, the pilot plant includes one of the two bottling units mentioned above, as required.
EDLC. Computer Controlled Liquid Packaging Teaching Unit. This unit allows the juices to be stored in containers suitable for transport and preservation, ensuring that they reach the final consumer with maximum quality and freshness. The Computer Controlled Liquid Packaging Teaching Unit, "EDLC", is a liquid and semi-dense products dosing machine based on dose delivery through a pneumatically-operated cylinder. The packer is responsible for filling the containers with the processed juice in an efficient and sanitary manner.
BMAF. Bottling Machine for Agroalimentary Liquid Products. An alternative to the previous unit is the Bottling Machine for Agroalimentary Liquid Products, "BMAF". This unit can only dispense liquid products, compared to the possibility of packaging semi-dense products from the EDLC. The bottling machine is crucial in the production line, since it is responsible for filling the containers with the processed juice in an efficient and sanitary way, ensuring the transportation and correct storage of the product.
Finally, the product is capped and sealed for its correct conservation in the following unit supplied.
EDMT. Capping Machine for Agri-food Liquid Products. The capper is responsible for placing the hermetic caps on the juice-filled containers, ensuring that they are securely sealed and that the product is protected against contamination and oxidation. This unit together with the bottling machine ensures that the final product is ready for distribution and consumption, maintaining its freshness and quality.
Depending on the required production and the characteristics of the fruits to be treated there are recommended the following elements: Additional recommended elements (Not included):
Once the crushed fruit is pressed in the Sheet Press for Liquid Products Extraction, "SPLE" or Hydraulic Press for Liquid Product Extraction, "HPLE" (only one of the two units is recommended) an unclarified juice is obtained, which, depending on the requirements, could be treated in an enzymatic process, previous step to the clarification of the juice in the Sheet Filter for Agri-food Liquid Products, "SFAF". This stage of the process guarantees the adequate preservation of the product, extending its shelf life and maintaining its freshness and natural flavor.
On the one hand, where fruits with high pectin content are used, enzymatic treatment with pectolytic enzymes can help to break down the pectin and improve juice clarity.
In addition, it may be necessary in certain cases to deactivate undesirable enzymes that could affect the quality or stability of the juice concentrate. For example, enzymatic deactivation of polyphenoloxidase (PPO) in fruits such as apples and pears can prevent oxidation and browning of the juice.
Another consideration is that enzymatic pretreatment can improve juice extraction by breaking down the cell walls of the fruit and releasing more liquid.
With these considerations in mind, you may choose to use the unit:
- TCAT. Temperature-Controlled Agri-food Tank. It is used to carry out enzymatic processes that help improve juice quality and flavor. The temperature control ensures optimal conditions for enzymatic activity, which allows for greater efficiency in the transformation of fruit into juice.
On the other hand, a mixer and homogenizer is available, where the clarified and concentrated juice in the Computer Controlled and Touch Screen Evaporator for Concentrating Agri-food Liquid Products, "ECAL/CTS", can be mixed in the Computer Controlled and Touch Screen Milk Homogenizer, "DMH/CTS" (not included in the plant).
If the required production capacity is limited, it is not necessary to use the homogenizer for the production of juice concentrate.
However, the homogenizer becomes more necessary if larger scale production is wanted, where a consistent and uniform production of the final product is desired. In addition, it allows mixing different ingredients and other fruit juices with the juice.
- DMH/CTS. Computer Controlled and Touch Screen Milk Homogenizer. Ensures uniform and homogeneous mixing of the product, which improves quality and stability by avoiding phase separation and maintaining a constant consistency. In addition, it helps to adjust the flavor and texture of the final juice concentrate.
If a high product flow is required, the use of a transit pump to pump and transport the intermediate products from the plant is recommended. The following unit can be considered for this application:
- TPAF. Transit Pump for Agri-food Products. This unit can be used with a wide variety of agri-food products and allows working in a wide range of flow rates.
Finally, during the whole production process, products and by-products are generated and can be stored in steel (not included) or polypropylene (not included) tanks suitable for working with agri-food products. The units that perform this function are:
- SSTAF. Stainless Steel Tank for Agri-food Products. Stainless steel tank designed for the storage of intermediate and final products in a plant. Its stainless steel construction ensures corrosion resistance and a hygienic surface. Its modular design and storage capacity make it ideal for efficient management of production processes.
- PTAF. Polyethylene Tank for Agri-food Products. Polypropylene tank designed for the storage of intermediate and final products in an industrial plant. Its polypropylene construction offers resistance to chemical corrosion and excellent durability, making it ideal for environments where agri-food substances are handled. Its lightweight and versatile design allows for easy installation and transport.
 Preferências de cookies
Preferências de cookies