At EDIBON, we are committed to strengthening skills as a strategic pillar for the competitiveness and social well-being of the European Union. Proper training not only boosts the economy but also enables individuals to fully participate in society and democracy.
MDUC Computer Controlled Machine Diagnosis Unit
INNOVATIVE SYSTEMS
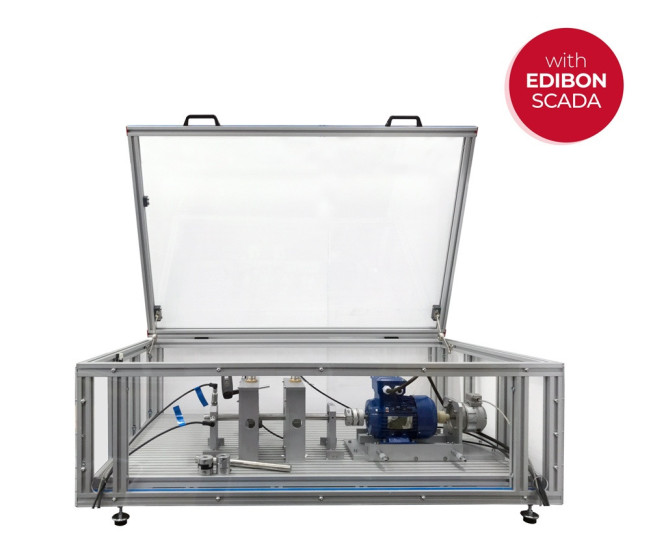
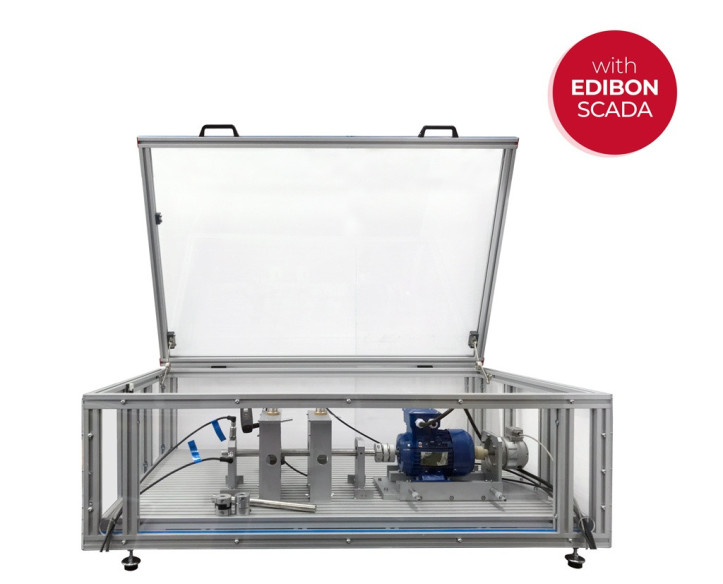
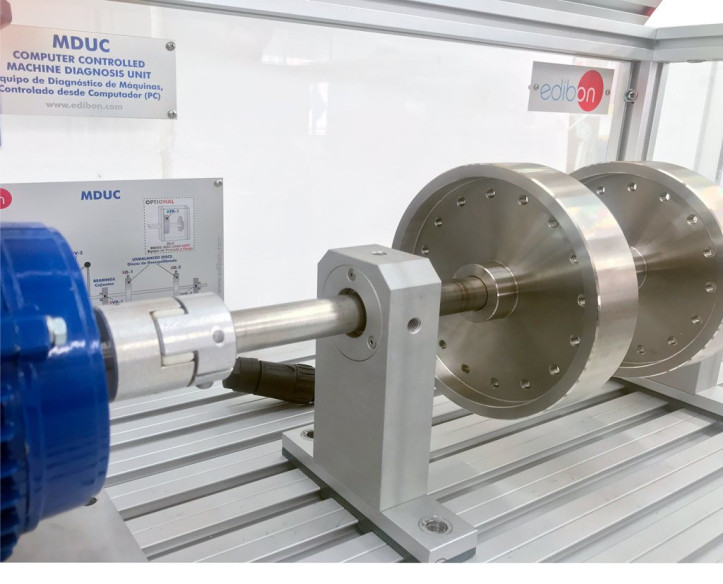
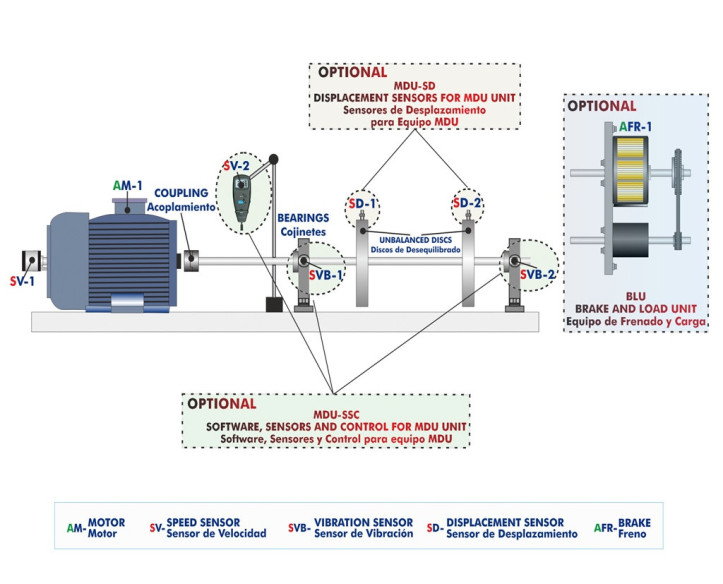
The Computer Controlled Machine Diagnosis Unit, "MDUC", of EDIBON, allows you to perform vibration measurement practical exercises, measuring the displacement, velocity and acceleration of vibrations in the time-frequency range.
Expansions
RELATED NEWS
General Description
The Computer Controlled Machine Diagnosis Unit, "MDUC", of EDIBON, allows you to perform vibration measurement practical exercises, measuring the displacement, velocity and acceleration of vibrations in the time-frequency range.
The Computer Controlled Machine Diagnosis Unit, "MDUC", includes the following elements:
- The MDU Base Unit, "MDU-UB".
- The Software, Sensors and Control for MDU Unit, "MDU-SSC".
- Displacement Sensors for MDU Unit, "MDU-SD".
Exercises and guided practices
GUIDED PRACTICAL EXERCISES INCLUDED IN THE MANUAL
- Assessment of the vibration state of a machine.
- Measuring the vibrations caused by unbalanced operation ofrigid rotors in 1 and 2 planes.
- Study of the basic essentials of the vibration measurement in shafts and bearings.
- Study of the basic magnitudes and parameters.
- Use of measuring sensors and instruments.
- Understanding the influence of speed and shaft and recorder arrangements.
- Learning to balance rigid shafts in operation and alignment between motor and bearing.
- Understanding and interpreting the frequency spectra.
- Learning about the different vibration signals.
- Applying the FFT analysis correctly.
- Measuring the speed, oscillation travel, oscillation speed and acceleration.
- Learning about the effects of alignment on different types of couplings.
- Learning about the effects of speed on vibration behavior.
- Learning about the effects of the balanced and unbalanced elastic rotor (MDU-SES kit required).
- Study of the variation of a typical vibration behavior (vibration velocity, frequency, amplitude, and phase) due to a fissure (MDU-SRS kit required).
- Identifying cracks and fissures in shafts through acceleration curves and order analysis (MDU-SRS required).
- Identifying a fissure through the variation of a vibration spectrum (MDU-SRS required).
- Estimating the life cycle of a roller bearing (MDU-SRBF required).
- Identifying faulty roller bearings (MDU-SRBF required).
- Checking the effects of roller bearing faults on outer and inner ring, or the roller bearing body on the vibration spectrum (MDU-SRBF required).
- Understanding the effect of ring gear hardness on claw couplings (MDU-SCO required).
- Comparing the curved tooth, bolt, flange or claw couplings (MDU-SCO required).
- Understanding the importance of belt tension in vibration behavior (MDU-SBD required).
- Checking the effect of the eccentricity in pulleys and the speed in vibration behavior (MDU-SBD required).
- Comparison between defective and non-defective belts (MDU-SBD required).
- Understanding and interpreting the frequency spectra in order to differentiate between defective and non-defective belts (MDU-SBD required).
- Identifying defects in the gears according to their vibration behavior (MDU-SSDG required).
- Learning about the effect of the toothed gear, the lubrication used and the wheelbase and the backlash (MDU-SSDG required).
- Identifying wear on the rod and piston (MDU-SCM required).
- Learning about the effect of bearing clearance and impacts (MDU-SCM required).
- Study of the vibrations of a centrifugal pump in operation (MDUSSCPrequired).
- Understanding the cavitation phenomenon in a centrifugal pump (MDU-SSCP required).
- Identifying vibrations caused by the movable vanes in the vibration spectrum (MDU-SSCP required).
- Measuring the pitch frequency between movable vanes (MDU-SSCP required).
- Measuring the blower vibrations (MDU-SSCP required).
- Learning about the effect of an asymmetric air gap on the vibration behavior and the electromagnetic and performance losses (MDU-SEV required).
- Learning about the effect of the electrical windings on vibration behavior (MDU-SEV required).
MORE PRACTICAL EXERCISES TO BE DONE WITH THE UNIT
- Many students view results simultaneously. To view all results in real time in the classroom by means of a projector or an electronic whiteboard.
- Open Control, Multicontrol and Real Time Control. This unit allows intrinsically and/or extrinsically to change the span, gains, proportional, integral, derivative parameters, etc, in real time.
- The Computer Control System with SCADA and PID Control allow a real industrial simulation.
- This unit is totally safe as uses mechanical, electrical and electronic, and software safety devices.
- This unit can be used for doing applied research.
- This unit can be used for giving training courses to Industries even to other Technical Education Institutions.
- Control of the MDUC unit process through the control interface box without the computer.
- Visualization of all the sensors values used in the MDUC unit process.
- By using PLC-PI additional 19 more exercises can be done.
- Several other exercises can be done and designed by the user.
SIMILAR UNITS AVAILABLE
7.4.3.- INSTALLATIONS AND MAINTENANCE TRAINING
MDU
The family of Machine Diagnosis Unit, "MDU", of Edibon, allows you to perform vibration measurement practical exercises, measuring the displacement, velocity and acceleration of vibrations in the time-frequency range.The MDU Base Unit, "MDU-UB",...
SUPPLEMENTARY EQUIPMENT
7.4.3.- INSTALLATIONS AND MAINTENANCE TRAINING
ADSG
Drive, Shaft, and Gear Alignment Unit
The Drive, Shaft, and Gear Alignment Unit, "ADSG", allows for studying the coupling and uncoupling, maintenance, repair of the related units and checking the operation with the following units:CGA. Combined Gear Assembly Unit.SGA. Spur Gear...
7.4.3.- INSTALLATIONS AND MAINTENANCE TRAINING
MDU
Machine Diagnosis
The family of Machine Diagnosis Unit, "MDU", of Edibon, allows you to perform vibration measurement practical exercises, measuring the displacement, velocity and acceleration of vibrations in the time-frequency range.The MDU Base Unit, "MDU-UB",...
7.4.3.- INSTALLATIONS AND MAINTENANCE TRAINING
MDU-MLB
Mobile Structure for MDU
The Mobile Structure for MDU, "MDU-MLB", is a robust structure designed to quickly and easily assemble the various elements of the MDU Base Unit, "MDU-UB" or the Computer Controlled Machine Diagnosis Unit, "MDUC", and thus assemble a mobile test...
7.4.3.- INSTALLATIONS AND MAINTENANCE TRAINING
MDU-SM
Top Table Structure for MDU
A bench-top structure consisting of a slotted table with anodized aluminum frames of 1100 x 770 x 820 mm.It has a transparent protective cover that protects against the rotating parts and allows us to observe the different experiments. The cover...
7.4.3.- INSTALLATIONS AND MAINTENANCE TRAINING
MDU-SSC
Software, Sensors and Control for MDU Unit
The aim of the vibration analyzer is to assess the machine diagnosis testing with the different kits related to the vibration interface technology.The system consists of two acceleration sensors, a speed sensor, a measuring amplifier with...
7.4.3.- INSTALLATIONS AND MAINTENANCE TRAINING
MDU-BLU
Break and Load Unit
The Break and Load Unit, "MDU-BLU", of EDIBON is a magnetic particle brake, a display unit and an electrical control. It is possible to precisely adjust the braking moment. The excitation current is used as a measurement of the braking moment and...
7.4.3.- INSTALLATIONS AND MAINTENANCE TRAINING
MDU-SES
Set of Elastic Shaft
The Set of Elastic Shaft, "MDU-SES", of EDIBON allows to study the behavior of an elastic rotor subjected to imbalance and balance of elastic rotors in operation. It is possible to study the resonance and the phenomena occurred in subcritical and...
7.4.3.- INSTALLATIONS AND MAINTENANCE TRAINING
MDU-SRS
Set of Rotating Shaft with Crank
It is important that fissures resulting from material fatigue in rotating machines are detected in good time before the breakage occurs, which usually leads to fatal consequences.The Set of Rotating Shaft with Crank, "MDU-SRS", consists of two...
7.4.3.- INSTALLATIONS AND MAINTENANCE TRAINING
MDU-SRBF
Set of Roller Bearings with Faults
To determine the remaining life cycle of a roller bearing and decide on its replacement, the slow variation of the vibration spectrum is analyzed. The spectral distribution will enable to draw accurate conclusions about the type of defect and its...
7.4.3.- INSTALLATIONS AND MAINTENANCE TRAINING
MDU-SCO
Set of Couplings
The Set of Couplings, "MDU-SCO", allows to compare the properties of different couplings such as curved tooth, bolt, flange and claw couplings.The vibrational behavior of the different types of couplings is important to draw conclusions about...
7.4.3.- INSTALLATIONS AND MAINTENANCE TRAINING
MDU-SBD
Set of Belt Drive
The belt drives are noiseless drive devices, have a long life and require little maintenance provided that its design, assembly and adjustment are correct.The Set of Belt Drive, "MDU-SBD", allows to study the conditions that cause vibrations or...
7.4.3.- INSTALLATIONS AND MAINTENANCE TRAINING
MDU-SSDG
Set to Study Damage in Gears
The Set to Study Damage in Gears, "MDU-SSDG", allows to study the vibrational behavior of gears with typical defects.For that purpose, gears with tooth defects and gears without defects are included, so a comparative study can be carried out. The...
Quality

AFTER-SALES SERVICE

 Cookie preferences
Cookie preferences